


 |
(MIDI player required) |
| Geography |
Location: Eastern Asia, northern half of the Korean Peninsula bordering the Korea Bay and the Sea of Japan, between China and South Korea
Geographic coordinates: 40 00 N, 127 00 E
Map references: Asia
Area:
total: 120,540 sq km
land: 120,410 sq km
water: 130 sq km
Area—comparative: slightly smaller than Mississippi
Land boundaries:
total: 1,673 km
border countries: China 1,416 km, South Korea 238 km, Russia 19 km
Coastline: 2,495 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
military boundary line: 50 nm in the Sea of Japan and the exclusive economic zone limit in the
Yellow Sea where all foreign vessels and aircraft without permission are banned
Climate: temperate with rainfall concentrated in summer
Terrain: mostly hills and mountains separated by deep, narrow valleys; coastal plains wide in west, discontinuous in east
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 m
highest point: Paektu-san 2,744 m
Natural resources: coal, lead, tungsten, zinc, graphite, magnesite, iron ore, copper, gold, pyrites, salt, fluorspar, hydropower
Land use:
arable land: 14%
permanent crops: 2%
permanent pastures: 0%
forests and woodland: 61%
other: 23% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 14,600 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: late spring droughts often followed by severe flooding; occasional typhoons during the early fall
Environment—current issues: localized air pollution attributable to inadequate industrial controls; water pollution; inadequate supplies of potable water
Environment—international agreements:
party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Environmental Modification,
Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Law of the Sea
Geography—note: strategic location bordering China, South Korea, and Russia; mountainous interior is isolated, nearly inaccessible, and sparsely populated
| People |
Population: 21,234,387 (July 1998 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 26% (male 2,800,857; female 2,669,250)
15-64 years: 68% (male 7,089,039; female 7,406,901)
65 years and over: 6% (male 387,011; female 881,329) (July 1998 est.)
Population growth rate: -0.03% (1998 est.)
Birth rate: 15.3 births/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Death rate: 15.57 deaths/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.44 male(s)/female (1998 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 87.83 deaths/1,000 live births (1998 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 51.32 years
male: 48.88 years
female: 53.88 years (1998 est.)
Total fertility rate: 1.6 children born/woman (1998 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Korean(s)
adjective: Korean
Ethnic groups: racially homogeneous; there is a small Chinese community and a few ethnic Japanese
Religions: Buddhism and Confucianism, some Christianity and syncretic Chondogyo
note: autonomous religious activities now almost nonexistent; government-sponsored
religious groups exist to provide illusion of religious freedom
Languages: Korean
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write Korean
total population: 99%
male: 99%
female: 99% (1990 est.)
| Government |
Country name:
conventional long form: Democratic People's Republic of Korea
conventional short form: North Korea
local long form: Choson-minjujuui-inmin-konghwaguk
local short form: none
note: the North Koreans generally use the term "Choson" to refer to their
country
abbreviation: DPRK
Data code: KN
Government type: Communist state; one-man dictatorship
National capital: P'yongyang
Administrative divisions: 9 provinces (do, singular and plural) and 3 special cities* (si, singular and plural); Chagang-do (Chagang Province), Hamgyong-bukto (North Hamgyong Province), Hamgyong-namdo (South Hamgyong Province), Hwanghae-bukto (North Hwanghae Province), Hwanghae-namdo (South Hwanghae Province), Kaesong-si* (Kaesong City), Kangwon-do (Kangwon Province), Namp'o-si* (Namp'o City), P'yongan-bukto (North P'yongan Province), P'yongan-namdo (South P'yongan Province), P'yongyang-si* (P'yongyang City), Yanggang-do (Yanggang Province)
Independence: 9 September 1948 Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK) Foundation
Day
note: 15 August 1945, date of independence from the Japanese and celebrated
in North Korea as National Liberation Day
National holiday: Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK) Foundation Day, 9 September (1948)
Constitution: adopted 1948, completely revised 27 December 1972, revised again in April 1992
Legal system: based on German civil law system with Japanese influences and Communist legal theory; no judicial review of legislative acts; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage: 17 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: KIM Chong-il [de facto]; note—President KIM Il-song was reelected
without opposition 24 May 1990 and died 8 July 1994, leaving his son KIM Chong-il
as designated successor; KIM Chong-il became General Secretary of the Korean
Workers' Party on 8 October 1997, but has not assumed the presidency
head of government: KANG Song-san is premier, but is in ill health; Vice Premier HONG Song-nam
has been acting premier since NA February 1997
cabinet: State Administration Council appointed by the Supreme People's Assembly
elections: premier elected by the Supreme People's Assembly
election results: NA
Legislative branch: unicameral Supreme People's Assembly or Ch'oego Inmin Hoeui (687 seats;
members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections: last held 7-9 April 1990 (next to be held NA); note—the term of the
Assembly expired in April 1995 without a new election and it has not been
convened since the death of KIM Il-song in July 1994
election results: percent of vote by party—NA; seats by party—the KWP approves a single
list of candidates who are elected without opposition; minor parties hold
a few seats
Judicial branch: Central Court, judges are elected by the Supreme People's Assembly
Political parties and leaders: major party—Korean Workers' Party (KWP), KIM Chong-il, General Secretary; Korean Social Democratic Party, KIM Pyong-sik, chairman; Chondoist Chongu Party, YU Mi-yong, chairwoman
International organization participation: ESCAP, FAO, G-77, ICAO, ICRM, IFAD, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, Intelsat (nonsignatory user), IOC, ISO, ITU, NAM, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO
Diplomatic representation in the US: none; note—North Korea has a Permanent Mission to the UN in New York, headed by YI Hyong-chol
Diplomatic representation from the US: none
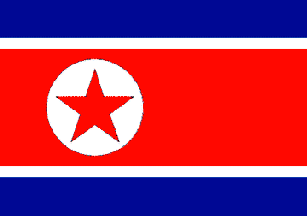
Flag description: three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (triple width), and blue; the red band is edged in white; on the hoist side of the red band is a white disk with a red five-pointed star
| Economy |
Economy—overview: More than 90% of this command economy is socialized; agricultural land is collectivized; and state-owned industry produces 95% of manufactured goods. State control of economic affairs is unusually tight even for a communist country because of the small size and homogeneity of the society and the strict rule of KIM Il-song in the past and now his son, KIM Chong-il. Economic growth during the period 1984-88 averaged 2%-3%, but output declined by an average of 4%-5% or more annually during 1989-97 because of systemic problems and disruptions in economic and technological links with the former USSR and China. The leadership has insisted on maintaining its high level of military outlays from a shrinking economic pie. Moreover, a serious drawdown in inventories and critical shortages in the energy sector have led to increasing interruptions in industrial production. Abundant mineral resources and hydropower have formed the basis of industrial development since World War II. Manufacturing is centered on heavy industry, including military industry, with light industry lagging far behind. Despite the use of improved seed varieties, expansion of irrigation, and the heavy use of fertilizers, North Korea is not yet self-sufficient in food production. Indeed, a shortage of arable lands, several years of poor harvests, systemic inefficiencies, a cumbersome distribution system, and extensive floods in 1995-96 followed by a severe drought in 1997 have resulted in increasingly serious food shortages. Substantial grain shipments from Japan and South Korea are offsetting a portion of the losses. North Korea remains far behind South Korea in economic development and living standards.
GDP: purchasing power parity—$21.8 billion (1997 est.)
GDP—real growth rate: -3.7% (1997 est.)
GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$900 (1997 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
agriculture: 25%
industry: 60%
services: 15% (1995 est.)
Inflation rate—consumer price index: NA%
Labor force:
total: 9.615 million
by occupation: agricultural 36%, nonagricultural 64%
Unemployment rate: NA%
Budget:
revenues: $19.3 billion
expenditures: $19.3 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (1992 est.)
Industries: military products; machine building, electric power, chemicals; mining (coal, iron ore, magnesite, graphite, copper, zinc, lead, and precious metals), metallurgy; textiles, food processing
Industrial production growth rate: -7% to -9% (1992 est.)
Electricity—capacity: 9.5 million kW (1995)
Electricity—production: 35.2 billion kWh (1995)
Electricity—consumption per capita: 1,499 kWh (1995)
Agriculture—products: rice, corn, potatoes, soybeans, pulses; cattle, pigs, pork, eggs
Exports:
total value: $912 million (f.o.b., 1996 est.)
commodities: minerals, metallurgical products, agricultural and fishery products,
manufactures (including armaments)
partners: China, Japan, South Korea, Germany, Hong Kong, Russia
Imports:
total value: $1.95 billion (c.i.f., 1996 est.)
commodities: petroleum, grain, coking coal, machinery and equipment, consumer goods
partners: China, Japan, Hong Kong, Germany, Russia, Singapore
Debt—external: $12 billion (1996 est.)
Economic aid:
recipient: an estimated $200 million to $300 million in aid from US, South Korea,
Japan, and EU in 1997
Currency: 1 North Korean won (Wn) = 100 chon
Exchange rates: North Korean won (Wn) per US$1—2.15 (May 1994), 2.13 (May 1992), 2.14 (September 1991), 2.1 (January 1990), 2.3 (December 1989)
Fiscal year: calendar year
| Communications |
Telephones: 30,000 (1990 est.)
Telephone system: system is believed to be available principally for government business
domestic: NA
international: satellite earth stations—1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and 1 Intersputnik
(Indian Ocean Region); other international connections through Moscow and
Beijing
Radio broadcast stations: AM 18, FM 0, shortwave 0
Radios: 3.5 million
Television broadcast stations: 11
Televisions: 400,000 (1992 est.)
| Transportation |
Railways:
total: 5,000 km
standard gauge: 4,095 km 1.435-m gauge (3,500 km electrified; 159 km double track)
narrow gauge: 665 km 0.762-m gauge
dual gauge: 240 km (standard and broad gauge) (1996 est.)
Highways:
total: 31,200 km
paved: 1,997 km
unpaved: 29,203 km (1996 est.)
Waterways: 2,253 km; mostly navigable by small craft only
Pipelines: crude oil 37 km
Ports and harbors: Ch'ongjin, Haeju, Hungnam (Hamhung), Kimch'aek, Kosong, Najin, Namp'o, Sinuiju, Songnim, Sonbong (formerly Unggi), Ungsang, Wonsan
Merchant marine:
total: 105 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 663,527 GRT/930,587 DWT
ships by type: bulk 7, cargo 87, combination bulk 1, multifunction large-load carrier
1, oil tanker 3, passenger 3, passenger-cargo 1, short-sea passenger 2
note: North Korea owns an additional 1 ship (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 15,143
DWT operating under the registry of Honduras (1997 est.)
Airports: 49 (1994 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
total: 22
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 15
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 2 (1994 est.)
Airports—with unpaved runways:
total: 27
2,438 to 3,047 m: 4
1,524 to 2,437 m: 5
914 to 1,523 m: 12
under 914 m: 6 (1994 est.)
| Military |
Military branches: Korean People's Army (includes Army, Navy, Air Force), Civil Security Forces
Military manpower—military age: 18 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
males age 15-49: 5,704,690 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—fit for military service:
males: 3,449,880 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
males: 175,181 (1998 est.)
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $5 billion to $7 billion (1995 est.)
Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 25% (1995 est.)
| Transnational Issues |
Disputes—international: 33-km section of boundary with China in the Paektu-san (mountain) area is indefinite; Demarcation Line with South Korea
This page last updated on 20 August 1999.
Designed by Britt A. Cartrite,
1999